Difference between Wire and Cable VS
In this section on wire vs cable, we will examine the fundamental difference between the two types of electrical conductors wire and cable
In the fields of electrical engineering and communication, the phrases “wires” and “cables” are seen rather often
However, individuals have a tendency to get the two words confused with one another since they appear similar but are, in fact, extremely distinct
In addition, we will provide you with a concise explanation of the distinction between wires and cables in the next section of this article
Now, let’s take a look at the most fundamental distinction that exists between wire and cable
The most fundamental and important distinction that can be made between wires and cables is that a wire only has one conductor, but a cable has several conductors
Despite this, these conductors are constructed out of a very standard material, which is either copper or aluminum
Wires are often exposed and twisted, and they may or may not be naked
However, some of the wires have a very thin film of PVC coating on them
Cable
In the case of cables, the individual strands are laid out in parallel and then either twisted or bonded together to create a single casing
Both an inner and an outer sheath are constructed for the goal of ensuring the user’s safety
The diameter of a wire is the unit of measurement for a wire
A gauge number is a measurement that is assigned to the wire and is based on the diameter of the wire
The larger the number of the wire’s gauge, the thinner the wire
The 10 and 20 gauge is considered to be the ideal gauge for usage in household applications
Bear in mind, however, that larger cables carry greater current and have the potential to cause harm to home items by blowing fuses
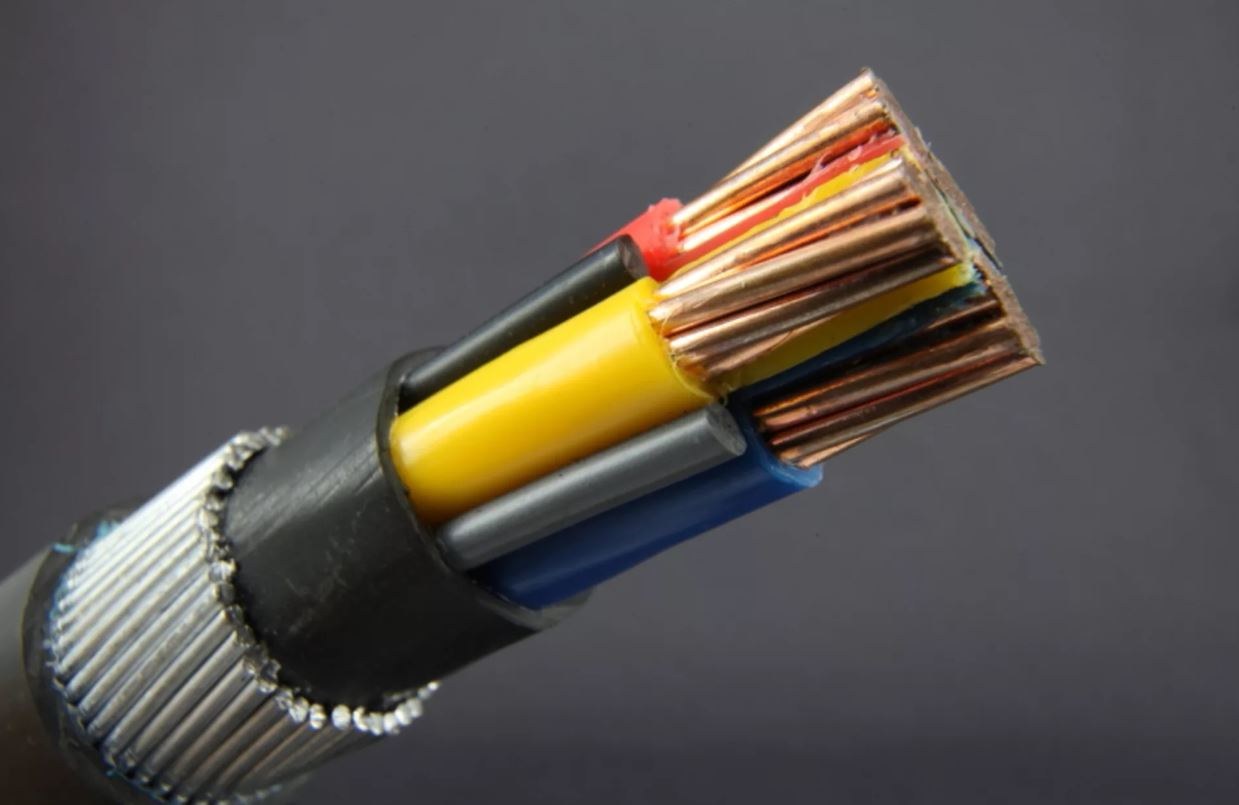
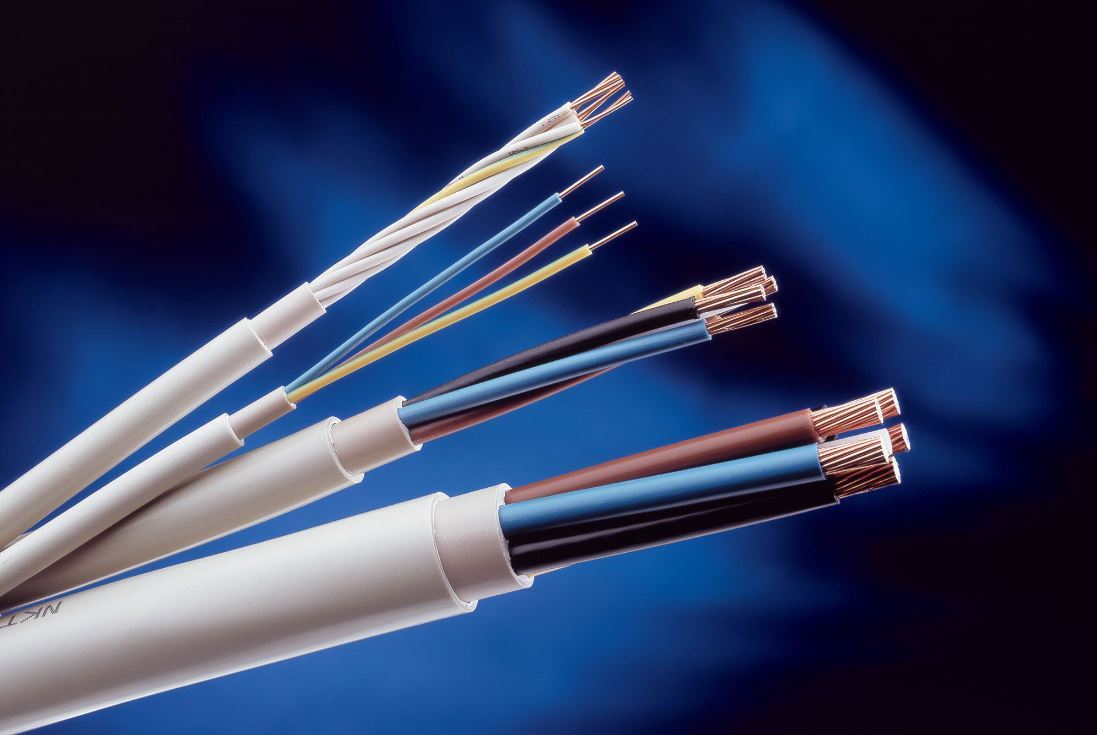
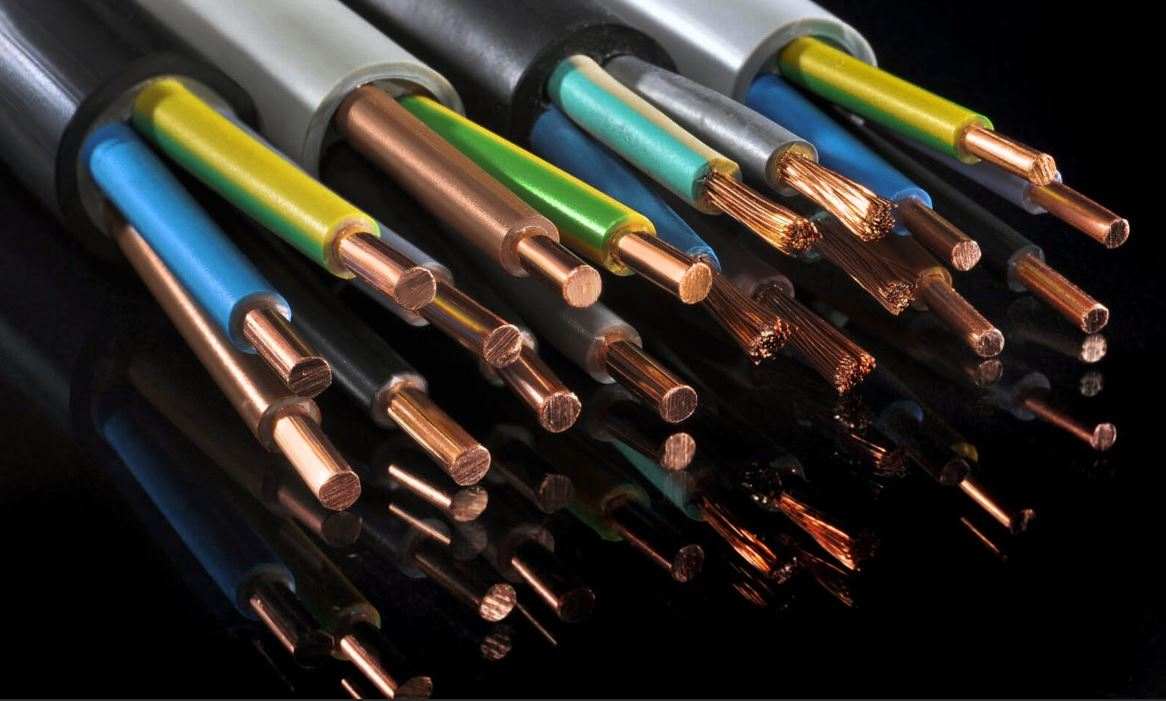
Cable A cable often has three sets of wires: a hot wire that carries the current, a neutral wire that helps to complete the circuit, and a grounding wire
The total number of wires that make up a cable and the diameter of those wires are both used to categorize the cable
Now, let’s take a look at the myriad ways that wire and cable can be put to use

Wire and cable
Heating jewelry, clothes, automobiles, or any industrially created components such as pins, bulbs, and needles requires the use of a wire because of its ability to convey electricity, support electrical loads, send telecommunication signals, and bear electrical loads
On the other hand, a cable can be utilized for the transmission of power, for the carrying of electrical signals, or for the transmission of telecommunication signals
After taking a cursory look at the many applications of wire and copper cable, we are now in a position to discuss the various types of wire and cable
Different kinds of electrical wires
Solid A solid wire is a single-conductor wire that may be insulated or left bare, and it is often shielded by a colored sheath
Solid wires are the most common kind of wire
This wire has a lower resistance than others, making it suitable for use in higher frequency applications
stranded: A wire that is stranded has multiple tiny wire strands that are twisted together to form a single cable
Stranded wire may be used for an extended amount of time and is utilized in situations that demand flexibility
The cross-sectional area of the standard wire is much bigger than that of the solid wire when compared to the latter

Electric wire and cable
Various Forms That Electrical Cables Can Take
A cable consisting of two cables that are twisted together to form a single unit is called a twisted pair cable
Because this twisting is able to reduce the noise that is caused by magnetic coupling, it is used in the transmission of signals
Data transfer and telephony are two of the most common applications for twisted pair cable
Multi-conductor cable: This kind of cable contains two or more than two insulated conductors, and the primary function of these conductors is to maintain the signal’s integrity
The term “balanced line configuration cables” may refer to cables with either twisted pair or multi-conductor configurations
Coaxial cable — A coaxial and network cable contains an inner conductor that is covered by insulating layers and is surrounding by a parallel outer foil conductor that is also shielded by insulating layers
Insulating dielectric material acts as a barrier between the cable’s two conductors, preventing electrical current from leaking between them
Due to the fact that its performance is more consistent than that of the twisted pair cable, these cables are often utilized in TV cable
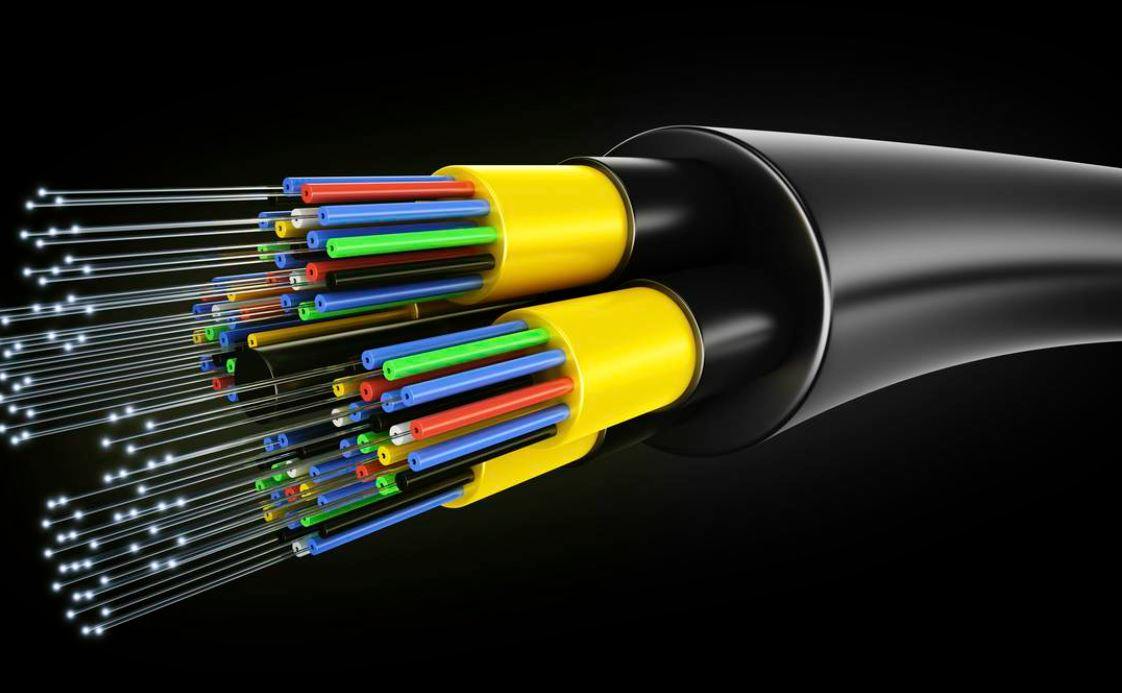
Fibre optic cable The signals are sent via a collection of glass threads in a fiber optic cable, which, in comparison to metal conductors, has a wider bandwidth
This implies that fiber optic cables are capable of transporting more information and data than metal conductors
As a result of this rationale, fiber optic cables are used rather of the more conventional copper cables

Norms that are applicable to both the wire and the cable
Any wires or cables that are ripped or otherwise damaged need to be replaced
Check that all of the wires and cables are polarized and that they have safety closures on them
Make sure that the wires and cables are out of the reach of youngsters, and if you are concerned about the safety of your children, switch to flame retardant cables made of Finolex
Refrain from putting wires and cables in areas where they might easily cause someone to trip
difference between wire and cable
When we talk about the difference between wire, conductor, and cable, the first thing we need to do is define when and how each of these things is employed
When planning an electrical installation work, it might be helpful to have an understanding of the distinctions and the ability to describe them properly
In order to prevent misunderstandings, we will concentrate on language that is specifically connected to applications in the electrical contracting business
WHAT EXACTLY IS WIRES? A single conductor is what makes up a wire, and it is often constructed of copper, aluminum, or even steel (for uses other than electrical)
Solid wire and stranded steel wire are the two most common forms of wire
Solid wire is a kind of electrical conductor that consists of a single strand of copper, aluminum, or another type of conductive metal that has been pulled into a string-like structure that is long and thin while remaining rigid
Because it has less resistance than other types of wire, solid wire is often employed in applications that need it to handle higher frequencies
Stranded wire is made up of many strands of solid wire that have been pulled into ultra-thin and flexible thread-like filaments
These filaments may be twisted or braided together to produce a single conductor that is equivalent in size and weight to the solid wire that they were derived from
Stranded wire is often coated and is an excellent choice for tasks that demand a greater degree of flexibility

CONDUCTOR Conductor is a word that refers to wire or wire filaments that do not have any coating or insulation separating them from one another
After the necessary jacket has been put to stranded wire, for example, the individual strands of wire that make up the stranded wire may be twisted or braided to create a single stranded conductor
The same may be said for the single strand of solid wire after it has been jacketed
Single conductors might be as tiny as 22 AWG or as massive as the wires classified in the MCM categories
As long as every strand of wire is uninsulated and in touch with the other wires, they may be made up of a single piece of wire or numerous strands of ultra-thin wire (filaments)
CABLE When attempting to provide a definition of a cable, the first thing that one must always keep in mind is that wire is one of the components that makes up a cable
Cables are groupings of two or more conductors made up of stranded or solid wire that are twisted, wrapped, or otherwise linked together in some other manner
These conductors are grouped together to form the cable discount
There are four primary varieties of cable: The term “twisted pair cable” refers to a configuration in which two cables are twisted together
Twisted pair cables have widespread use in the fields of telecommunications and professional audio engineering, as well as in recording studios, theaters, and intercom systems
A multi-conductor cable is comprised of many individual cables that are bundled together and insulated from one another
Because the insulation lowers the amount of interference that occurs between the cables, multi-conductor cables are a common option for use in the process of data transmission

Coaxial cable is characterized by its construction, which consists of a solid core conductor and an outside layer foil conductor that surrounds it
Both layers are separated from one another by an insulating material
These cables are often used in broadcast media, such as television and radio, in addition to other modes of communication
As the price of multi-conductor category/ethernet cables and fiber optic cables has fallen down and as their capacity to transfer signals with fewer and fewer interruptions has improved, coaxial cable is gradually losing its market share to these more modern alternatives
The term “fiber-optic cable” refers to a collection of wires that either partially or wholly consists of optical fibers
Optical fibers are very fine wires that can transmit more data at a quicker rate conventional alloy cables
These wires may be constructed from either glass or plastic
Although fiber optics are the wave of the future when it comes to transporting data and communications, they cannot completely replace copper cables since they are unable to transmit electricity
Having acquired knowledge on the many cable and wire varieties that are available
Find out what the differences are between wire, conductor, and cable in this lesson
It is important to keep in mind that individual wire strands make up a cable’s conductors, and that cables cannot exist without conductors
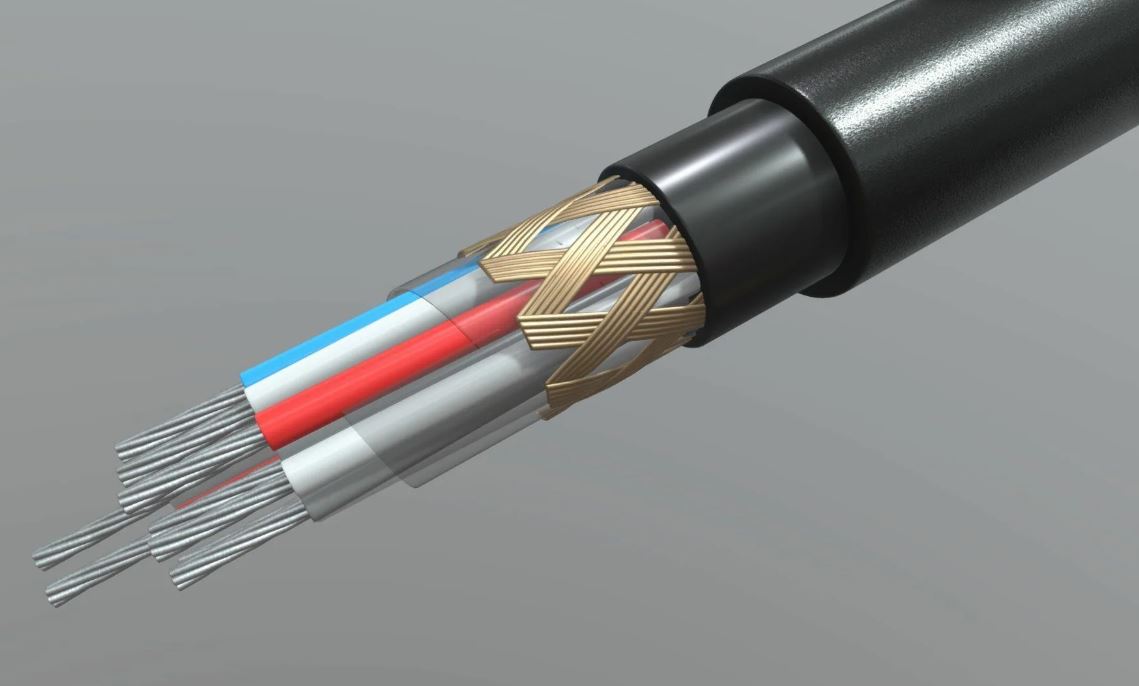
Conductors may consist of a single strand of wire or numerous strands of wire, as long as the multiple strands are not isolated from each other
The wire can be one thicker strand for a solid wire or finer strands (filaments)
Additionally, a cable is composed of more than one conductor, each of which has to be insulated from the other conductors in the cable
wire vs cable
Cable vs wire is a comparison that can perhaps be answered by regarding wire as a sub component of cable
Both phrases are among the most common ones used in the fields of telecommunications, electronics, and electrical appliances
Wires may be thought of as the “inner component” (conductors) that are used in cables
These cables are insulated on both the inner and the outer sides, hence wires are the “inner component
” Conductors are the materials that are often utilized in the production of cables and wires
Sturdy top metal such as copper and aluminum are selected because of their ability to efficiently transmit electrical current

A contrast between cable and wire The primary distinction between wire and cable is that wire conductors are bundled together inside of cable, while each every strand of wire in wire only has a single conductor
Whereas a wire often only has one conductor and is not insulated, cables are made up of numerous conductors, each of which has its own insulation
Cables are also more flexible than wires
When communicating over long distances, cables are often more effective than wires, whereas wires are more suitable for shorter distances
Multiple wires are twisted around each other to create a single layer, which results in the formation of cables
It is for reasons of safety that cables are constructed with a sheath that is both internal and lateral
There are primarily four different kinds of cables, and they are as follows: twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, multi-conductor cable, and fiber-optic cable
Cables find their most common use in day-to-day life, including in cable television, for telecommunications reasons, in theaters and studios, and so on
A single conductor is used to make up each wire (copper or aluminum profile)
They have a thin covering of polyvinyl chloride, which is a synthetic plastic polymer that is manufactured via a process called polymerization
This layer protects them from the elements
There are primarily two different kinds of wires, which are solid and stranded respectively
Solid wires are made up of a single thin conductor that is stranded several times
These wires are rigid yet have the capacity to bend
Stranded wires are made up of many thin conductors that are twisted together to create a single casing
This gives the wires their distinctive appearance

What exactly is a cable? Multiple stranded filaments of wire are twisted together to produce a single cable wire
Cables are made of these wires
It is insulated from both the inside and the outside, both internally and outwardly
There are four different sorts of cables, and each type of cable has a distinct mechanism that is tailored to the use for which it is intended
The following is a list of several types of cables: The term “twisted pair cable” refers to a configuration in which two individual cables are combined and twisted together to produce a single cable
Internally, a solid conductor gives coaxial cable its shape, while an outside layer of foil protects the conductor
The number one cable may be found on televisions, radios, and other types of broadcast media
Multi-conductor cable: The cables are linked together to create a multi-conductor cable, which is then utilized for the transmission of information after having been used to make the multi-conductor cable
The bandwidth of optical fiber cables is much greater than that of conventional cables
As a result, optical fiber cables are increasingly being used in lieu of cables with metallic conductors
Electrical impulses are often transmitted via the use of cables
In most cases, this will consist of two or more wires that are linked to one another
There is an extensive variety of cables available to suit almost every application imaginable
The transfer of electricity, electrical appliances and gadgets, communication, and a variety of other uses often call for the utilization of cables
They are visible in radio and television broadcasts because they are utilized extensively in the process of transmitting signals over vast distances, which is why they are used

What exactly is a wire? A single conductor or a cluster of conductor filaments that are wrapped around each other in an insulating casing to prevent unintended connections make up a wire, as was mentioned before
The transmission of telecommunications signals and electrical impulses often takes place via the use of wires
There are two primary categories of wires, solid and stranded
Stranded wires are made up of two or more strands of single conductor that are wrapped around each other
Solid wires are made up of a single conductor that is stretched out across its whole length
The low resistance of solid wires makes them the go-to choice at higher frequencies
On the other hand, the durability and adaptability of stranded wires make them the better choice for extended periods of time
In comparison to solid wires, stranded wires have a greater cross-sectional area since they are composed of a group of two or more individual strands
It is possible to calculate the length of a wire based on its diameter
The diameter of the wire will serve as the basis for determining the gauge number that will be allocated to the wire
The greater the gauge number, the more the wire will be reduced in thickness
10 and 20 are the most common gauge numbers used in gadgets and appliances for the home
Large wires are often used in commercial and industrial settings; however, they should never be utilized in domestic appliance settings since this can cause the fuse to blow due to the increased current flow

The Principal Distinctions That Separate Wire and Cable
A wire is either made up of a single conductor strand or a group of conductor strands that are twisted around each other to make a single strand, while a cable is made up of several conductors that are twisted around each other to form a single strand
Since cables are insulated on both of their ends, they are a more secure option than wires
To put it more simply, we may say that cables are not visible owing to their insulation, but wires are visible because they are exposed
In comparison to wires, the strength capacity of cables is much greater
On the other hand, they are more expensive than cables
Transmission of telecommunications and the conveyance of electrical impulses are two of the many uses for cables
6
Cables have a longer shelf life than wires do because of the insulation that is included inside the cables
Wires are used in the day-to-day activities of home tasks to deliver power (lights, ceiling fans, air conditioners, etc
) and communications signals
Despite the fact that the words “wire” and “cables” are often interchanged with one another
Keep in mind that wires are the building blocks of cables, since this will help you differentiate between the two
Wires also have a suitably wide variety of uses in many different fields
There is no meaningful difference between “wires” and “cables,” hence the term is artificial
When working with cable and wire, one must exercise caution in order to prevent getting into a potentially dangerous scenario
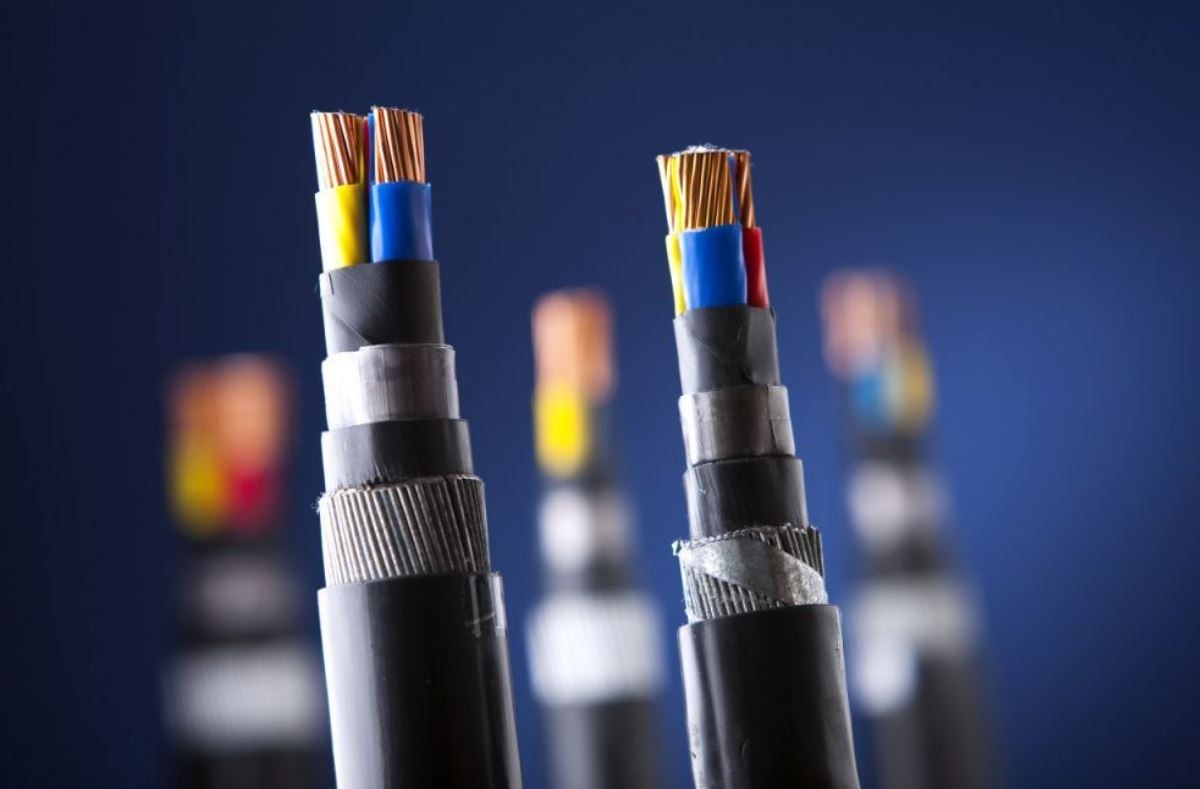

wire and cable difference
The words “wire” and “cable” are often interchanged in the area of electrical engineering to refer to the same item
Nevertheless, there are significant differences between wire and cable that need to be taken into consideration for the success of an electrical installation
The term “wire” always refers to a single conductor, while “cable” refers to a number of conductors that are insulated together in a single jacket
This is the primary distinction between the two terms
Conductors are often manufactured out of copper, aluminum, or some other kind of conductive metal in each scenario
One significant exception to this rule is a cable that is constructed of optical fibers and is known as a fiber optic cable
Therefore, what exactly is a wire? Even though a wire has more than one strand, it still only functions as a single conductor regardless of the number of strands it has
Solid wire and stranded wire are two main varieties of wire that are used
When compared to stranded wires, solid wires only have a single strand, while stranded wires have numerous strands
Wires that are stranded are more flexible than wires that are solid, which are often harder
It may be uninsulated or covered with a sheath for further protection
In both business and residential structures, electrical current and communications signals are often transported via the use of wires
They provide an outstanding performance at higher frequency ranges
Wires have the advantage of being less expensive than cables, which means that one may use them to save money on their energy bills
In industrial applications that need for the heavy-duty strength that cables provide, wires are not employed instead of cables
The number of the wire’s gauge as well as its capacity to conduct electricity are both factors that are considered while classifying wires
They may be used on their own or as a component of a cable at the same time
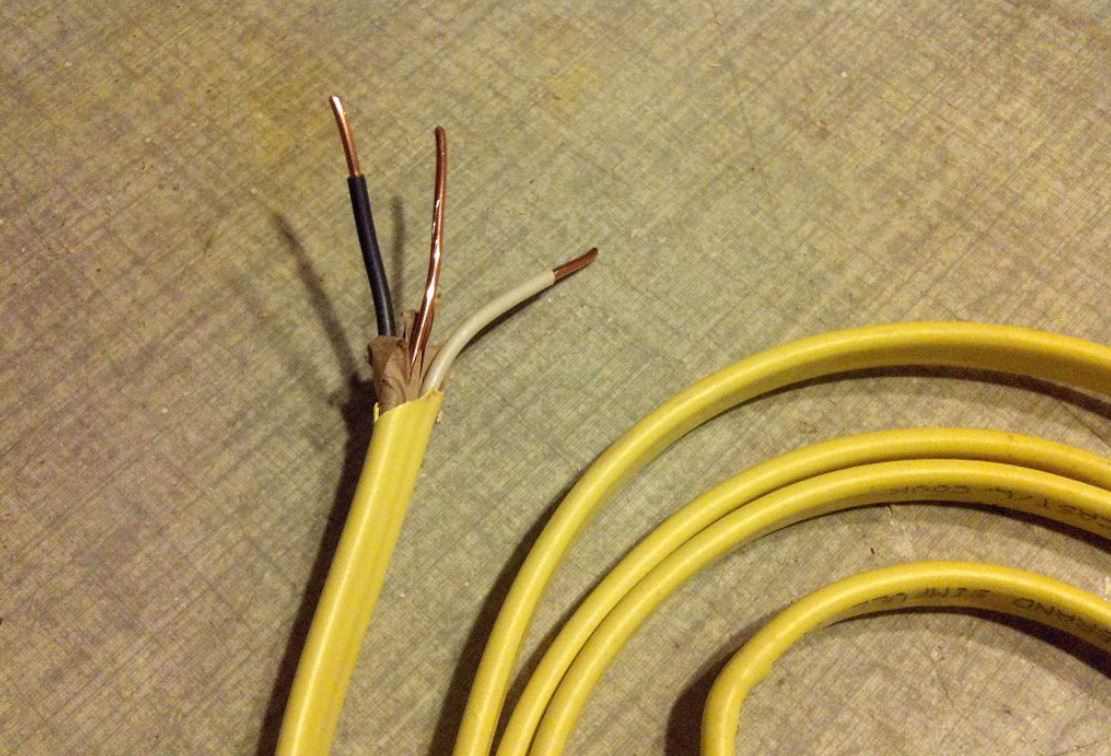

And, can you explain what a cable is? Cables, just like wires, are used to transport electrical impulses from one location to another
On the other hand, they have a wider range of flavors
There are many different kinds of cables, but some of the more frequent ones include twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, multi-conductor AC power cables, and fiber optic cables
Each of these cables use a unique mechanism that is tailored specifically to its intended function
Different signals are carried by each of the two conductors in coaxial cables
Conductors in thunderbolt cables are responsible for transporting electricity as well as a variety of communications
The signal is carried across the majority of cables by the conductors cooperating with one another
There is a dizzying array of cables suitable for every conceivable application available on the market today

Cables are used in a variety of contexts, including but not limited to power and signal circuits in electronic equipment, power transmission and illumination in buildings, long-distance communication beneath the sea, and other similar contexts
The gauge number, the number of wires, and the color of the jacket make up three of the most important categories of a cable
On the other hand, depending on any other characteristics, there could be some further classes
what is the difference between wire and cable
In order to understand what the difference between wire and cable is, we should know that, a wire is a single conductor while cable is a group of two or more conductors
The terms “wires” and “cables” are often used interchangeably, despite the fact that there is a significant conceptual gap between the two
Keeping in mind that wires are only one component of cables is one way to tell them apart from one another
In addition, the applications for wires are significantly more varied
A single strand or group of strands made of an electrically conductive material, typically aluminum or copper, is what we mean when we talk about a wire
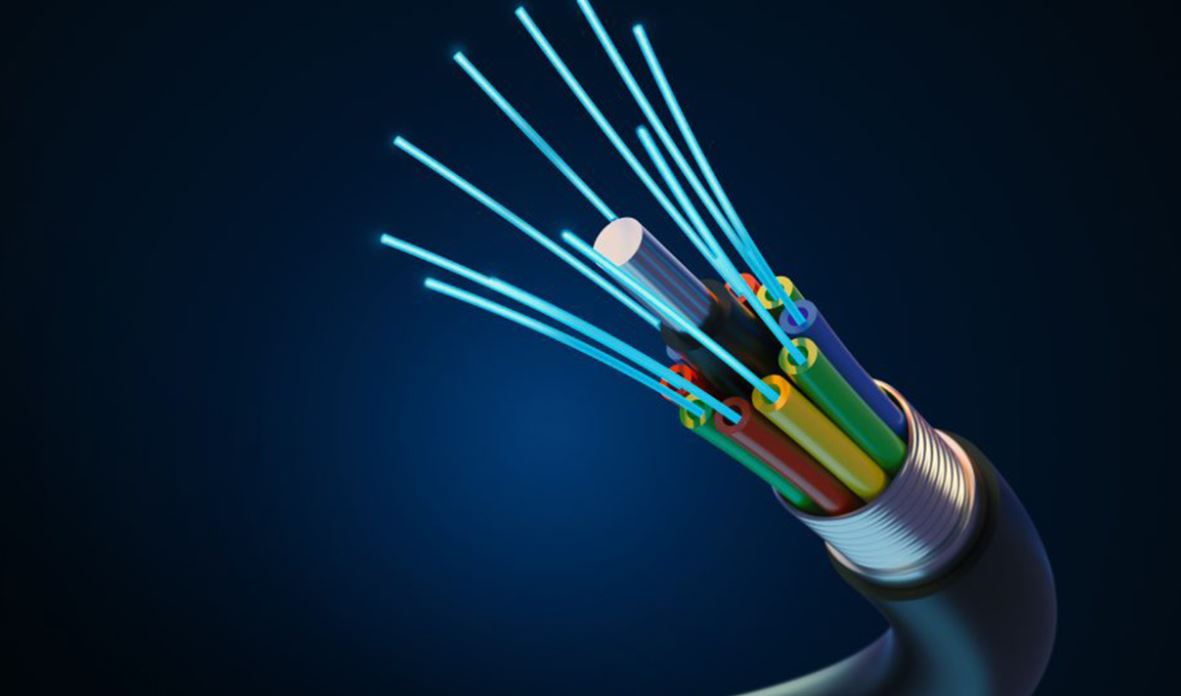
On the other hand, a cable is made up of two or more insulated conductors and may either be exposed or protected by an outer covering
The fact that a wire is often open to observation while a cable is typically covered in insulation is the most straightforward method for telling the two apart
There are primarily two categories of wires, which are solid and stranded
Generally speaking, a solid wire is a very long stretch of a single conductor
Multiple elongated strands of wire are twisted together to create a stranded wire
Solid wires have a low resistance and are ideal for use in higher frequencies, while stranded wires have a longer life owing to their flexibility and may be used for a longer amount of time than a single conductor
Solid wires are ideal for use in lower frequencies
Wires are most often employed to transport electrical and telecommunications information; but, they have a wide variety of other applications as well, including supporting mechanical loads, providing heat, and even being used in jewelry and clothing

In most cases, a cable is composed of two or more wires that are twisted, braided, or connected together in some manner
They often have insulation rather than none at all, which affords them more protection in comparison to simple wires
The transmission of electrical and telecommunications signals is the primary function of cables
There are many different kinds of cables, such as twisted pair cable, multi conductor cable, coaxial cable, and fiber optic cable
The primary purpose of a twisted pair cable is to carry signals and consists of two cables that are twisted around one another
Control applications are ideal for the utilization of multi conductor cables, which consist of many individual conductors that are individually insulated from one another
The signal that is transmitted along the two conductors of a coaxial cable is not the same
This type of line is known as an unbalanced line, and the performance on an unbalanced line is more consistent than the performance on a twisted pair cable
There are three varieties of fiber optic cables, which are as follows: plastic fibre – used for sending audio, multi-mode fibre – used for sending data, and single mode fibre – seen only under a microscope and has the best performance
wire or cable difference
When electricians do electrical work using wire or cable the underlying reasons based on which they choose between the two is in fact the differences that make them appropriate for particular purposes
they term it “electrical wiring,” which suggests that wires are involved
However, what they really fish through the walls from device to device are wires
So, what exactly occurred with the wires? They must still be there or we wouldn’t be able to make any links to them
When it comes down to it, distinguishing between wire and cable is not too difficult
Electrical cables are nothing more than bundles of wires that have been encased in insulation that is resistant to heat and moisture
The actual conducting wires, with the exception of the ground wires, are each separately covered with insulation, therefore this configuration offers an additional layer of protection for those wires
It also makes it simpler to monitor their whereabouts and progress
When you go to buy electrical cable, it will be identified not only by the size of the wire but also by the number of wires that are contained within the cable sheathing
Several Distinct Categories of Electrical Wires Copper is often used for the construction of electrical lines because it is a good conductor of electricity and because it is a requirement that electrical cables be constructed of a metal that can conduct electricity
Aluminum is an option for use in high-voltage and industrial applications, but it is not now used as one of the materials for electrical wiring in homes, despite the fact that this was the case in the early 1900s for a brief period of time
When it comes to wires, the diameter of the wire, as determined by its American Wire Gauge (AWG) number, is the most crucial characteristic for an electrician
(AWG is an abbreviation for American wire gauge; hence, it is synonymous with the wire gauge
) Lower gauge numbers indicate bigger wire diameters, and the higher the current that a given wire can safely carry before it begins to overheat is directly proportional to the gauge number
In domestic wiring, some typical wire gauges are 14, 12, 10, and 8 AWG, with 12 AWG being the most frequent
The most common wire gauge, however, is 14 AWG
In most cases, only electricians are able to work with wire gauges less than 8
There are Numerous Varieties of Electrical Cables
The number of conducting wires that are included inside a wire cable is the aspect of that cable that is considered to be the most significant

Every single residential circuit is grounded in today’s world, and each and every appliance is required to be connected to a ground wire; However, the ground wire itself is not considered to be a conductor
As a result, a cable with two conductors will have two insulated wires (typically black and white) in addition to a ground wire, while a cable with three conductors will have three insulated wires (typically red, black, and white) in addition to a ground wire
Another way to classify the electrical cable is according to its sheathing
The coating on interior residential cable is often made of nylon, and the cable may either be designated as THHN (heat-resistant) or THWN (standard) (water-resistant)
It is not uncommon to come across cables that have dual ratings and are resistant to both heat and water
If you require an electrical cable to perform outdoor wiring or to bury, you need UF-B (underground feed) cable, which is covered with PVC sheathing
This kind of cable is specifically designed for these types of applications
You will need NM-B (nonmetallic) cable in order to do wire work in a moist interior environment, such as a laundry room, for example
NM-B may be used for the majority of wiring projects indoors, but it should never be used outside

How to Track Down the Required Wire and Cable Because the electrical code is highly particular about which wire gauge and which kind of cable are required for various situations, it is best to get the advice of a certified electrician if you have any questions about this matter
Once you have an idea of what you want, the following will help you locate it on the shelves of the store: A pair of digits that are separated by a slash are used on the label that is attached to a roll of electrical wire to indicate the AWG and the number of conductors
For instance, a cable with 12/2 gauge has two conductors of 12 AWG, but a cable with 10/3 gauge has three conductors of 10 AWG
The unidentified ground wire is present in all of the low-voltage cables with the exception of a few of them
If you are going to use the cable outdoors, look for the UF-B label on it
If you are going to wire a bathroom or laundry room, look for the NM-B indication instead
Some of the low-voltage cable that is used for landscape lighting has the mark DBR, which indicates that it may be buried directly underground

wire and cable difference in hindi
The hindi association of wire and cable engineers defined the difference between optic wire and copper cable as follows: Copper cable and fiber optics both contain the ability to transfer signals, however copper cable does so in the form of electrical pulses, whilst fiber optics are capable of transmitting signals in the form of light pulses
This is the primary distinction between the two
The fact that copper wire and fiber optics have completely different names is another significant distinction between the two
Copper wire is the primary component of a copper cable
Fiber optics, on the other hand, may be made up of a single strand of glass fiber or many strands
The following descriptors are used by this association to describe copper cable: Copper cables are a kind of guided media that are mostly made up of copper wires that enable for the transfer of data from one end to the other
Due to the fact that copper wire is conductive, it has been used extensively as a medium for the transfer of data over the last 50 years
The mobility of electrons in copper cables is what allows data to be conveyed across these lines
Copper cable enables the transfer of data in the form of electrical pulses, and this is the reason for its popularity
Copper wiring is widely recognized as the most suitable element for use in the case of electrical apparatus

When telephones were first established in 1876, a significant surge in the need for copper wires as electrical conductors followed shortly after
Copper is a material that has great creep qualities, which show to be helpful when used in the process of cable connections
Copper has a higher resistance to corrosion than other metals, which is something to keep in mind when comparing it to other metals
After going over the description of copper cable and how it makes it possible for signals to be sent, let’s have a look at how the association that deals with fiber optics defines fiber wire and cable and how it makes it possible for signals to be transmitted in the form of light pulses
These are made up of multiple strands of glass or silica and can be very thin or very thick
These are dielectric waveguides, however they operate at optical frequencies rather than electromagnetic ones
The transmission of electromagnetic energy in the form of photons is accomplished via the use of fiber optics, which is based on the concept of total internal reflection (light particles)
The core of a fiber optic cable is made of glass, and it is encased with plastic cladding that has a lower refractive index than the core
Following is an explanation of the primary distinctions that exist between copper cable and fiber optics
The data transmission speed of a fiber cable is far greater than that of a copper cable, which is the primary distinction that can be made between copper cables and fiber optics

Copper wires have a data transmission speed that is almost 31 percentage points slower than fiber connections
When data is sent through a copper cable, it does so in the form of an electrical pulse, which is caused by the movement of electrons in the cable
In contrast, the transmission of data occurs as a result of the movement of photons in fiber optics, and as a result, the data is transmitted in the form of light pulses
The bandwidth that can be offered by a copper cable is much lower than that which can be delivered by fiber optics
Therefore, a copper cabling system satisfies the requirements set out by the industry and offers a performance of up to 10 Gbps
Fiber optics, on the other hand, thanks to the large bandwidth it possesses, has better performance of up to 60 Tbps and even higher
Copper cables require much more power than 10 watts of energy during normal operation, but fiber optic cables use far less power—approximately 2 watts of power for each user—during normal operation
Copper wire has an average lifetime of around 5 years since it is susceptible to damage from changes in temperature as well as other elements in the surrounding environment
However, the lifetime of fiber optics ranges anywhere from 30 to 50 years

Because fiber optics are more difficult to tap than copper connections, using them is desirable from a safety and security standpoint
As a result of this factor, the usage of fiber optics for the transport of data is becoming more commonplace right now
When compared to copper wire, the speed at which data can be sent with fiber optics is much higher
Fiber optic cables have higher costs associated with their installation and maintenance than copper cables do
As a whole, following this debate, we can reach the conclusion that fiber optics are superior in terms of durability and dependability, and as a result, they have very effectively replaced copper cables in the modern period
In the past, copper cables were used extensively However, there is mounting evidence that fiber optics may successfully replace copper cables in a variety of applications
It is important to note, however, that the greater costs of installation and maintenance might occasionally result in a decreased demand for fiber optics

difference between drive by wire and cable
In order to understand what the differences between drive by wire and drive by cable are
We need to initially understand what these are and where they apply
Drive by wire is a system in which the accelerator pedal, which is controlled by the driver, is depressed to activate the throttle
In order to communicate with the ECU, this makes use of a potentiometer throttle sensor
This enables the computer to overrule the driver and provides improved engine control by taking into consideration a greater number of factors
This has the potential to increase throttle responsiveness, horsepower, and torque, as well as reduce emissions and lead to better fuel efficiency
On occasion, everything at once
Drive by wire was preceded by the technology known as drive by cable
It attached a throttle cable to the pedal so that the user could manually control the opening of the throttle plate and the amount of air that was let into the engine
In automobiles with fuel injection, you would then feel the amount of throttle opening as well as the volume of air, as well as the pressure and temperature of the air, to determine the position of the throttle and determine the amount of fuel and the time to use
This method is not proactive like drive-by-wire; rather, it operates in a reactive fashion
Because of this, many manufacturers are moving toward the drive-by-wire system
It is possible that the end user will find it more difficult to service, but the performance and longevity will undoubtedly be enhanced as a result
wire and cable the difference
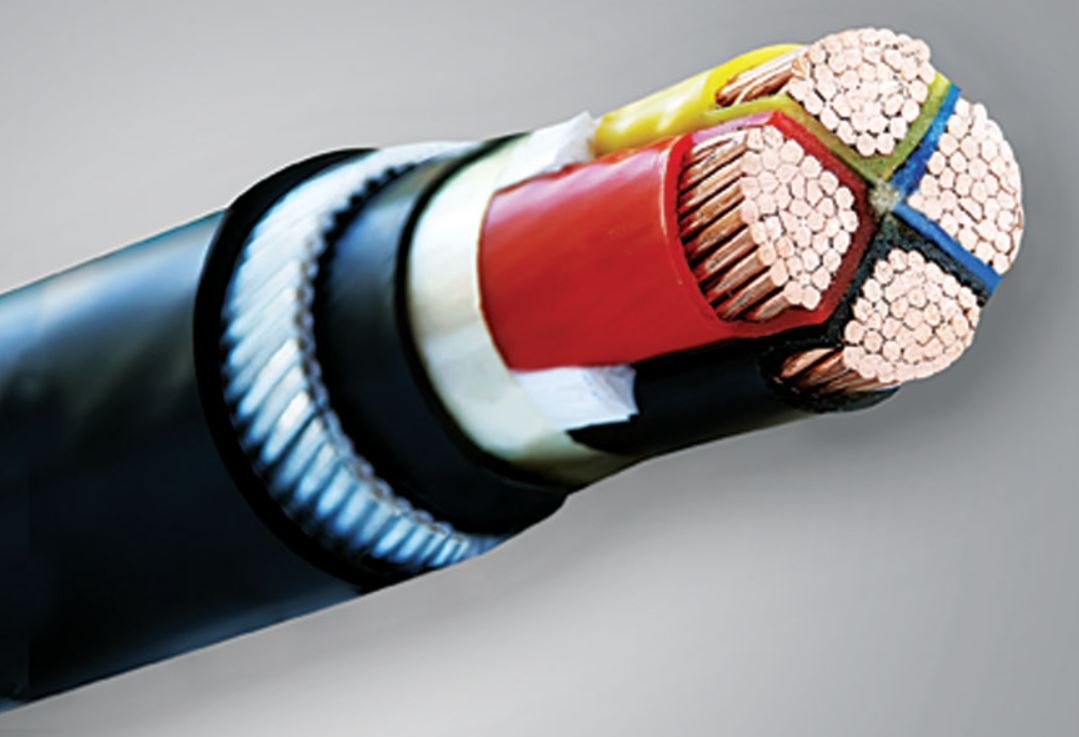
A wire is defined as one electrical conductor, while a cable is defined as a group of individually insulated wires (conductors) encased together in the sheathing
In the following paragraphs, the distinctions between wire and cable will be discussed in further detail
The segment of the wire or cable that conducts electricity is encased in sheathing, which is a non-conducting substance having protective characteristics
Even though wire is an excellent conductor, it nevertheless has the potential to exhibit some resistance
Copper, gold, and aluminum are just few of the materials that may be used in the production of wires and cables
Different resistances are shown by each of the materials
If two wires are produced from the same material but one is thicker than the other, the thicker wire will have a lower resistance

The wire’s resistance is subject to proportional shifts whenever there is a change in either the wire’s temperature or its length
The diameter of the wire’s metal conductor is what’s meant to be indicated by the term “wire size
” When selecting the size of the wire, it is necessary to take into consideration the gauge of the wire, the capacity of the wire, and the purpose of the wire
If the wire is too thin, then an excessive amount of current will be allowed to pass through it
This will lead the wire to lose more power, measured in watts, due to the high resistance that it presents
Solid and stranded wires are the two types that may be classified as single-conductor wires (also called braided)
Solid wire is more rigid than other types of wire and has better electrical conductivity
Stranded wire is made up of multiple smaller wires that are woven together
Because stranded wires are less likely to break when subjected to repeated flexing, you’ll typically find this type of wire utilized in mobile phone chargers
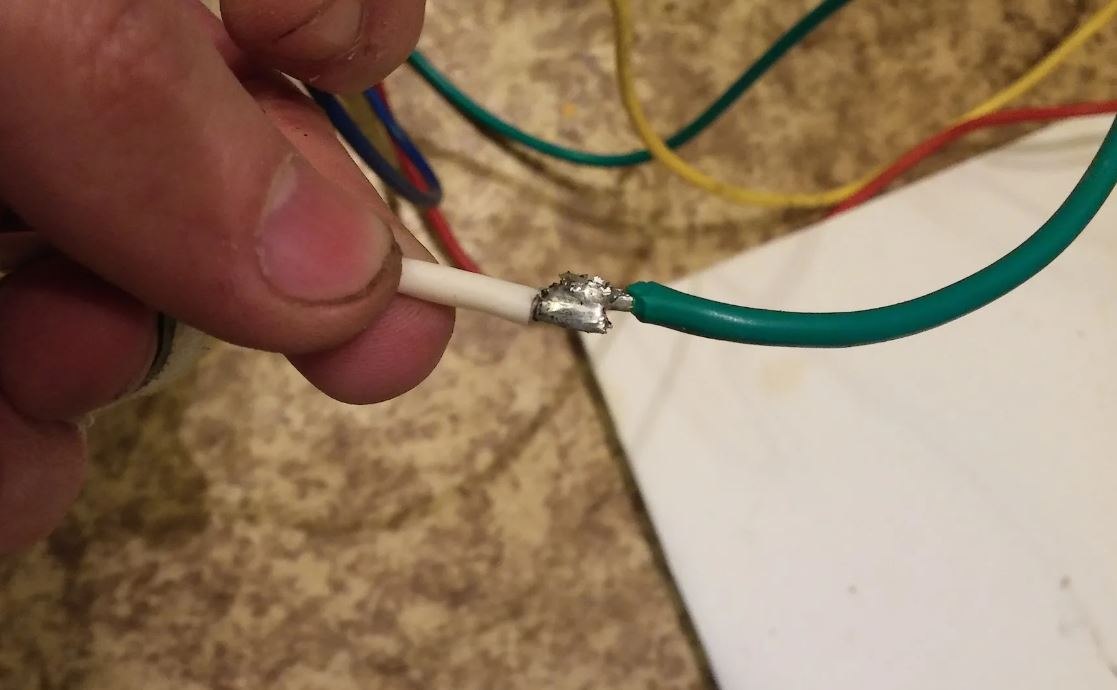

cable As was discussed before, a cable consists of a collection of insulated wires that are sheathed together in a casing
In most cases, a cable will have at least one hot wire, one neutral wire, and one grounding wire
The hot wire is the one that carries the current
A cable’s classification is determined by the number of wires it includes as well as the size and gauge of those wires
The cables are identified by a string of letters, which is then followed by a number, a dash, and one more number
The letters provide information regarding the type of insulation
The first number gives an indication of the resistance of the wires that are contained within the cable
The number that comes after the dash gives an indication of the total number of individual conductors that are contained within the cable
If a G appears after the final number, this indicates that the cable has an additional wire that does not carry current and serves as a ground
AC Power Cords are used to transfer current and voltage from a household power supply to an electronic device, typically an AC to DC power supply, in a manner that is safe and reliable
The individually insulated conductors are housed within a protective outer jacket that is more long-lasting and are equipped with connectors on either one or both of their ends

Along the jacket is typically where information such as the conductor size and count, current and voltage rating, temperature rating, and agency approvals are printed
A multi-conductor cable is a type of stranded wire that differs in that each cable contains anywhere from two to sixty individual conductors inside of a single jacket
Within the jacket, there may be either stranded conductors or solid conductors wound together in a bundle
These cables have a variety of applications and can be used to connect heavy appliances, as well as in audio systems, medical electronics, and more
A ribbon cable is made up of a number of single-conductor wires that are connected to one another in a parallel fashion to form a ribbon
Due to the fact that the conductors may be detached from the ribbon, it is also referred to as zip wire
Instead of being covered in a single protective jacket like the other varieties of cables, the wires in this kind of cable are insulated on an individual basis
The central conductor of a coaxial cable is insulated, and it is encased within a braided wire shield that is encased within a resilient outer jacket or sheathing
When two or more three-dimensional linear forms share an axis, this configuration is referred to as coaxial
This type of transmission line is capable of carrying electrical signals at high frequencies with minimal signal loss
The transmission of cable television signals, the establishment of broadband internet networking connections, and the coupling of radio transmitters and receivers to their antennas are all examples of possible uses
The outer plastic sheath, the woven copper shield, the inner dielectric insulator, and the central copper conductor make up the components that make up the coaxial cable
Speaker cable consists of two or more electrical conductors, commonly copper, each of which is separately insulated by a layer of plastic or rubber
Electrically speaking, the two wires are identical; nonetheless, they are labelled so that the right polarity of the audio stream may be determined
When making electrical connections between speakers and amplifier sources, speaker cable is the kind of cable that is employed
Electrical properties can be broken down into three categories: resistance, capacitance, and inductance
Because of the low resistance, more of the power from the source can pass through the speaker coil, resulting in a louder sound
2 differences between wire and cable
We have a lot of electrical wire and cable in our home, but when others ask us what the 2 primary differences are between wires and cables, we often get perplexed and look at them as if they have a totally blank expression on their face
It is vital that you should have some understanding about it if you want to utilize either electrical wires or cables effectively so that you may give electrical connections in your house
If you do not have any knowledge about it, you will end up getting the incorrect product
“Wires and Cables” play a crucial part in your day to day existence
They are are commonly utilized in electrical and communication equipment
In point of fact, wires and cables are not at all comparable to one another in any way
Wires and cables are used extensively in the electrical industry, and their primary purpose is to transport electrical current from one location to another
In the following paragraphs, we are going to provide an in-depth discussion of the distinctions that exist between wires and cables

A Distinction Can Be Made Between Wire and Cable A wire consists of a single conductor, but a cable is composed of two or more conductors and all of the individual wires are wrapped in a single conductor
This is the primary distinction between wire and cable
Wires for Electrical Appliances Wires for electrical appliances are typically found inside cables
The number of gauges or millimeters used to measure a wire’s diameter
If the gauge is low, the wire will be of a greater thickness
The 10 and 20 gauge is considered to be the ideal gauge for usage in household applications
Cables are made up of conductors, which are typically wires
Copper and aluminum are the typical metals used in the production of electrical wire because of their low cost and low resistance respectively
Keep in mind at all times that larger cables carry greater current and have the potential to cause harm to home appliances by blowing their fuses

Wires differ not only in their material and diameter or gauge, but also in the kind of insulation they have and the amount of electrical capacity they have
Users are protected by grounding wires, which have a yellow coating and provide a channel to the ground that has a low resistance from the appliances
Wire Lettering The primary insulation types of individual wires are denoted by a variety of letters, including THHN, THWN, THW, and XHHN, among others
The following National Electrical Code (NEC) standards are outlined in these letters for your reference:
insulating material made of thermoplastics
Resistance to high temperatures
High heat resistance (up to 194 degrees Fahrenheit)
W — Designed for use in damp environments
N – Coating made of nylon, resistant to the effects of oil and gas
X is an artificial polymer that is resistant to flames
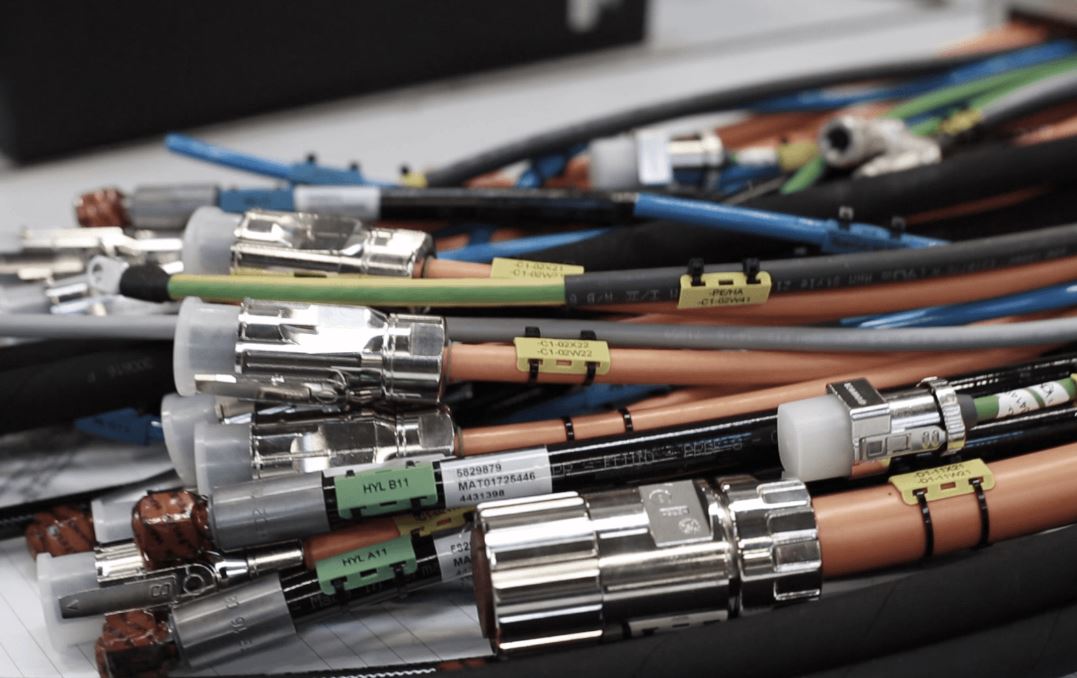

The following is a list of the various types of electrical wires that are utilized during the building process of a brand new home:
Wires that are Triplex
Main Feeder Wires
Wires for Feeding the Panels
Sheathed Conductors Made of Non-Metal
Single Strand Wires
The Meanings Behind the Different Colors of Wires The term “hot wire” refers to the black wire, which is typically found in electrical outlets and switches
The term “red wire” refers to the same thing as “hot wire
” They are utilized as the legs for the switch
Additionally, red wire is used to connect the wires of two hardwired smoke detectors to one another
Blue and Yellow Wire: Blue and yellow wire, sometimes referred to as hot wires, are used for pulled-in conduit
Blue and yellow wire are also known as hot wires
The blue wire is utilized for applications involving a 3-4 way switch, while the yellow wire is used for the switch legs that operate fans, lights, and so on
White Wire: The white wire is the neutral wire and is always used
Green and Bare Copper Wire: Green and bare copper wires are the only types of wires that are ever used for grounding and earthing 02
Electrical Cables A cable is a group of two or more insulated conductors that is used for the transmission of electrical power or signals
Cables may carry both electricity and communications
Every cable has three distinct kinds of wires: the first wire is used to transport current, the second wire is used to construct a closed loop, and the third wire serves as the grounding wire
In most cases, the conductor is categorized according to the gauge number, the wire number, and the color
There are numerous different configurations available, and each one is determined by the intended use
The conductor has to be utilized in regions that are exposed to extreme mechanical stress and offer greater protection than wires
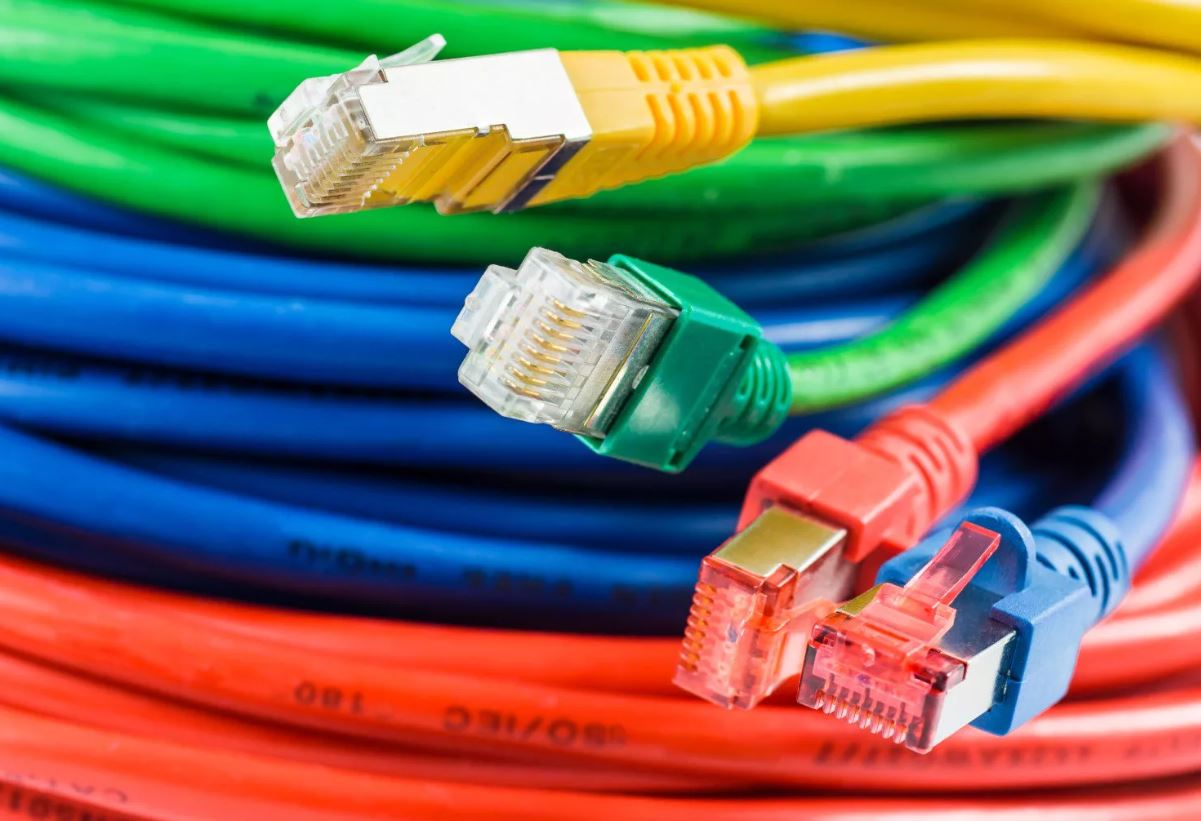
Electrical cables come in a variety of colors, and there are also several distinct types

Cables’ Assigned Color Codes It is possible to determine whether the cable insulation is active, neutral, or earth conductors by using a color coding system for the cable insulation
The NEC does not provide any color recommendations (National Electrical Code)
It is crucial to be aware of the cable color coding standards that are in effect in your location
The standards for cable color coding vary depending on the country or region
The following is a list of the many kinds of electrical cable that are used throughout the building process of a brand new home:
Coaxial cable
a cable that is buried directly
Flexible cable
Heliax cable
able encased in a non-metallic sheath cable encased in a metallic sheath
Multicore cable
Linked cables
Cordage that is portable and ribbon cable
Cable with a shield
a solitary cable a kind of structured cable
Twin and earth cable using the Twinax format

Wire and cable are used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, as well as for data and communication purposes
Metal, which is responsible for the wire’s ability to carry electricity, is the primary component of electrical wire
The following is a list of the several metals that are often used in the production of electrical wires and cables: Lid/Tin Aluminum Gold Copper Silver The terms wires and cables are used pretty much interchangeably, but in reality, they are quite distinct from one another
One method for telling the difference between the two is to keep in mind that cables are made up of wires
In addition, wires have a sufficiently broad range of applications
A single strand or a collection of strands made of an electrically conductive substance, often aluminum or copper, make up a wire
Wires may be single or multi-stranded

In contrast, a cable is made up of two or more insulated conductors (wire) and may either be naked (unprotected) or coated
The two are most easily distinguished from one another by the fact that a wire is typically open to observation, whereas a cable is almost always sheathed in insulation and has a larger diameter than a wire does








